14 Foods That Look Like the Body Part They Are Good For
Fueling your body with food packed with nutrition plays a key role in maintaining a healthy and optimally functioning body. Beyond this, though, could our food actually be telling us more about our bodies than we realize?
As it turns out, many of the foods we eat have an undeniable resemblance to different parts of the body. What’s even more interesting is that these food doppelgängers can play an important role in keeping those body parts optimally running.

1. Carrots Look Like Eyes
Have you ever heard that carrots are good for your eyes? I know growing up that I was told this hundreds of times as an incentive to clear the bright-orange vegetables from my plate. It turns out carrots really do carry many nutrients beneficial to vision. Carrots are high in antioxidants, specifically, beta-carotenes and lutein. In the body, this beta-carotene is converted to vitamin A, which is essential to the pigment in your eye to help you see at night. 1
Further studies have shown lutein can help maintain healthy eyesight and protect against macular degeneration and the development of cataracts. 2,3 In addition to all these great benefits, when carrots are cut into coins, they resemble the iris of an eye, making it clear to see which body part they support the most.
2. Tomatoes Look Like a Heart
Like the heart, tomatoes are red in color, and when you look at the inside, they contain different chambers. Not only do tomatoes look like a heart, they also promote heart health. Tomatoes contain a nutrient called lycopene, which can help reduce your chances of getting heart disease. Studies show lycopene can lower several heart disease risk factors, such as free-radical damage, total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol levels, and even increase good HDL cholesterol. 4,5

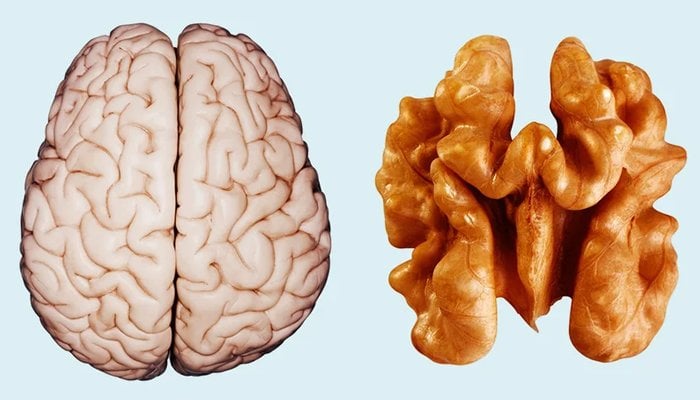
3. Walnuts Look Like a Brain
One food that has an uncanny resemblance to the organ it supports is walnuts. Walnuts mimic the construct of a brain through the appearance of two hemispheres and its outer folds and wrinkles.
Walnuts are beneficial to the brain as they are a good source of omega-3, antioxidants, folic acid, and vitamin E. Research shows the nutrients in walnuts can help reduce oxidative damage and inflammation in the brain and increase processing speed, mental flexibility, memory, and learning. 6,7
4. Sliced Mushrooms Look Like Ears
When slicing mushrooms, if you turn it sideways, you may notice a striking similarity to your ear. Ears contain three bones, which are essential to hearing because hearing depends on the vibrations of these bones. That means to have good hearing, you must have strong bones. Luckily, mushrooms are high in vitamin D, which is essential to keeping these bones healthy. 8
5. Ginger Looks Like a Stomach
Feeling queasy? A commonly used natural remedy to ease nausea and upset stomach is ginger. Not only can ginger help calm the stomach, but it also takes on a similar shape to the organ.
Gingerol, which is the main bioactive compound in ginger, gives the vegetable its strong taste and scent and has been deemed responsible for much of its medicinal properties. Gingerol has powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, which improve digestion and support the release of regulating hormones to calm your body and reduce nausea. 9
6. Celery Looks Like Bones
Celery’s long stocks have more in common with your bones other than just the appearance; they also naturally contain sodium, just like bones. Likewise, celery is high in calcium and silicon, which help regenerate and strengthen damaged bones. Celery even contains vitamin K, which plays an important role in bone health and helps fight against osteoporosis. 10
7. Grapes Look Like Alveoli
Another food with an unquestionable resemblance to the organ it helps is grapes. Grapes have a remarkable similarity to alveoli. Alveoli are the tiny sacs within our lungs that allow oxygen and carbon dioxide to move between the lungs and the bloodstream.
Grapes also contain a particular type of flavonoid called anthocyanins, which research has found protects the lungs against damage, preserving their functionality and reducing the risk of developing respiratory diseases. 11
8. Sideways Bananas Look Like a Smile
When grinning ear to ear, you may just have a smile as big as a banana. Whether you’re holding a banana up as a smiley face, pretending it’s a phone, or watching someone slip and fall on a peel, bananas make us laugh and lift our moods, but not just because of their appearance.
Bananas contain an amino acid called tryptophan. When digested, tryptophan gets converted into a neurotransmitter called serotonin, which is a mood-regulating chemical in the brain. Increased levels of serotonin can help regulate mood, decreasing anxiety and potentially leading to more feelings of happiness. 12
9. Sliced Onions Look Like Blood Cells
Sliced onions sure look a lot like the blood cells in your body. Onions are an excellent source of flavonoids, which are powerful antioxidants with anti-inflammatory benefits. By reducing inflammation in veins and arteries, onions can boost blood flow and heart health. 14
Additionally, onions are also rich in B vitamins, including folate and pyridoxine, which play a critical role in red blood cell production.

10. Sweet Potatoes Look Like a Pancreas
The configuration of the sweet potato resembles the shape, as well as promotes healthy function, of the pancreas. Sweet potatoes are high in beta-carotene, which is an antioxidant that protects tissues in the body, including the pancreas, from damage associated with cancer or aging.
One of the functions of the pancreas is maintaining the body’s blood glucose. Diabetes is the most common disorder associated with the pancreas. And, sweet potatoes can help balance blood sugar in diabetics because it contains adiponectin. Adiponectin is a protein hormone that has the ability to improve metabolism and insulin regulation. 13
11. Red Wine Look Like Blood
Historically, red wine has always been symbolic of blood, which makes sense given how much the two look alike. Red wine is rich in antioxidants and polyphenols, including resveratrol. Studies have shown resveratrol can lower blood pressure as well as improve your blood profile by reducing LDL cholesterol and increasing HDL cholesterol. 15,16 Red wine also contains a blood-thinning compound, which reduces blood clots associated with stroke and heart disease.
12. Beans Look Like Kidneys
More specifically, kidney beans, and as you could probably guess, kidney beans got the name due to their resemblance to real human kidneys. If you have healthy kidney function, kidney beans are full of minerals, vitamins, and antioxidants, which can contribute to kidney and whole-body health.
Kidney beans are also a terrific plant-based source of protein. They are rich in fiber and B vitamins that help in cleaning your kidneys, removing toxins and waste out of the body, and helping the urinary tract function better. However, those with reduced kidney function will want to be careful to limit their intake of beans due to their high levels of phosphorus.
13. Olives Look Like Ovaries
Beyond looking like ovaries, olives assist with their health and function. Olives contain an abundance of phenolic antioxidants as well as the anti-cancer compounds squalene and terpenoid. Researchers have investigated the effect of olives in the diet and have found that a higher intake of olive oil may help reduce the risk of ovarian cancer. 16
14. Cut Strawberries Look Like Teeth
When cutting a strawberry down the middle, the pattern inside is reminiscent of the roots of a tooth. Strawberries can, in fact, have an effect on your teeth due to their abundance of vitamin C. Vitamins C, along with other antioxidants found in strawberries, can aid in fighting periodontal gum disease and help reduce inflammation by warding off harmful bacteria. 17
Strawberries also contain malic acid, which acts as a double-edged sword. Although malic acid can help whiten the enamel on your teeth, it is still an acid, meaning that overtime, it can also wear down the tooth’s enamel.
Foods That Look Like the Body Part They Are Good For: Recap
Turns out the saying “you are what you eat” may hold more truth than originally thought. Although each of these foods is important in maintaining whole-body health, it seems their benefits in the body may be more than just a happy accident.
Coincidence or not, finding connections between the food you eat and your body can add a fun and fresh new way to look at healthy eating.




 7 Signs Your Body is Seriously Low on Collagen (not just wrinkles)
7 Signs Your Body is Seriously Low on Collagen (not just wrinkles) Health Expert: "Turmeric Doesn't Work (unless...)"
Health Expert: "Turmeric Doesn't Work (unless...)" 3 Warning Signs Your Probiotic Supplement is a Total Waste
3 Warning Signs Your Probiotic Supplement is a Total Waste

